With the rapid evolution of technology and the rise of digital innovation, LED displays have become integral to our everyday environments. Whether it’s in advertising, live events, corporate meetings, or outdoor signage, their versatility and superior performance make them indispensable. Among the critical parameters that define the quality of an LED display are refresh rate and resolution. While they both play pivotal roles in the viewing experience, their functions and impacts are distinctly different.
This article explores these two aspects in depth, shedding light on how they influence LED display performance and offering insights to help you choose the right display for your needs.
What Is Refresh Rate in an LED Display?
1. Definition of Refresh Rate
The refresh rate of an LED display refers to the number of times the screen updates its content every second. Measured in Hertz (Hz), it directly affects how smooth and fluid the visual experience appears. For instance, a 60Hz refresh rate means the screen refreshes 60 times per second.
2. Importance of Refresh Rate
A higher refresh rate enhances the screen’s ability to handle motion smoothly, making it ideal for dynamic and fast-paced visuals. Here are some examples where refresh rate plays a critical role:
- Gaming: High refresh rates reduce motion blur and input lag, delivering a smoother and more responsive gaming experience.
- Live Sports: In sports broadcasts, a high refresh rate ensures every movement is captured with precision, creating an immersive viewing experience for audiences.
- Advertising Displays: For outdoor and dynamic content, high refresh rates maintain smooth transitions and animations, grabbing viewers’ attention.
3. How Is Refresh Rate Achieved?
The refresh rate depends on the display’s drive circuit and control system:
- Drive Circuit: This component controls when and how each LED pixel is lit. Using precise timing and synchronization, it ensures smooth image updates.
- Control System: The control system processes incoming data, converts it to a compatible format, and sends it to the drive circuit for display.
Advanced technologies like hardware acceleration and improved algorithms further boost refresh rates, reducing lag and improving performance.
4. Refresh Rate and Power Consumption
While higher refresh rates offer better performance, they also consume more power. Each update requires energy, and frequent updates increase overall power consumption. Manufacturers address this by optimizing drive circuits, using energy-efficient LEDs, and introducing power-saving modes. For users, striking a balance between refresh rate and energy efficiency is essential, depending on the specific use case.
What Is Resolution in an LED Display?
1. Definition of Resolution
Resolution defines the number of pixels on an LED display and is a measure of its clarity and detail. Expressed as a combination of horizontal and vertical pixels (e.g., 1920×1080), it determines the sharpness and quality of the visuals.
2. Importance of High Resolution
Higher resolution provides more detail and clarity, making it essential for applications where visual fidelity matters:
- HD Video Playback: High-resolution displays ensure every detail of the video is crisp and lifelike.
- Image Processing: In industries like graphic design and photography, high resolution accurately reproduces colors and textures for a realistic visual experience.
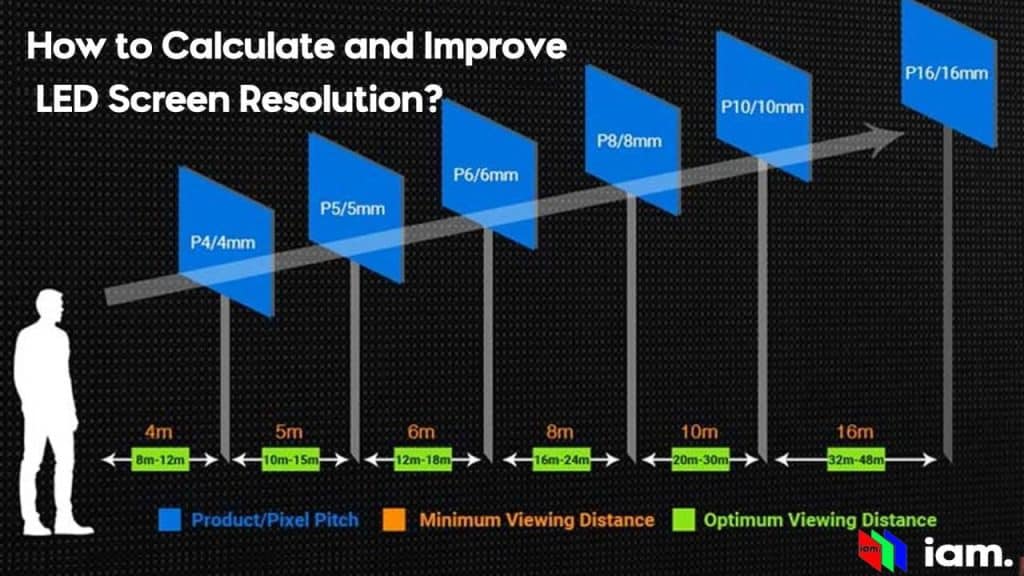
3. How Is Resolution Achieved?
Several factors influence an LED display’s resolution:
- Pixel Pitch: The distance between individual LEDs, known as the dot pitch, is a key determinant of resolution. Smaller pitches mean more LEDs per unit area, resulting in higher resolution.
- Driver ICs: These integrated circuits control the brightness and color of individual LEDs, ensuring precise image rendering.
- Image Processing Algorithms: Techniques like super-resolution enhance lower-quality content to achieve better visual outcomes.
4. The Role of Display Size in Resolution
Resolution is also impacted by display size. For the same resolution, a larger screen may result in less sharp visuals because each pixel covers more space. Solutions include reducing pixel pitch, using advanced splicing technologies to combine multiple displays, or employing image processing techniques to enhance perceived resolution.
Refresh Rate vs. Resolution: Understanding the Differences
Although both refresh rate and resolution influence an LED display’s performance, they cater to different aspects of the viewing experience.
1. Functional Differences
- Refresh Rate: Determines how smooth motion appears on the screen. It’s critical for applications with fast-moving visuals, like sports or gaming.
- Resolution: Determines the clarity and detail of images and videos, essential for scenarios like HD content playback or professional presentations.
2. Application Scenarios
- Refresh Rate: High refresh rates are crucial for live sports, fast-paced video games, or any scenario where smooth transitions are vital.
- Resolution: High resolution is essential for detailed visuals, such as in movie theaters, art installations, or high-end conference displays.
For example, in an e-sports tournament, players prioritize high refresh rates for fast reactions, while in a cinematic setting, audiences value high resolution for immersive visuals.
3. Connection Between Refresh Rate and Resolution
While distinct, refresh rate and resolution work together to enhance the overall performance of an LED display. High refresh rates ensure smooth motion, while high resolution delivers detailed and sharp imagery. Balancing both parameters is essential for achieving optimal results.
Choosing the Right LED Display: Factors to Consider
When selecting an LED display, consider the following factors:
1. Application Scenario
- Advertising: High resolution is key for static or slow-moving content like advertisements. A refresh rate of 60Hz or higher paired with a high resolution ensures eye-catching displays.
- Conferences: Displays used for presentations need balanced refresh rates (120Hz or higher) and resolutions to handle a mix of static and dynamic content.
- Live Events: For sports or concerts, prioritize a refresh rate of 120Hz or more to capture motion effectively, while maintaining sufficient resolution for clarity.
- Exhibitions: High-resolution displays (e.g., 4K or 8K) with refresh rates of 144Hz or above are ideal for showcasing stunning visuals.
2. Budget Considerations
High refresh rates and high resolutions increase costs, so prioritize features based on your needs and budget. For limited budgets, focus on the parameter that aligns best with your primary application.
3. Future Trends
Technological advancements are driving higher refresh rates (e.g., 240Hz or 360Hz) and ultra-high resolutions (8K, 16K). Staying informed about emerging trends ensures you invest in displays that remain relevant in the long term.
Conclusion
Refresh rate and resolution are critical parameters that shape the performance of LED displays. While the refresh rate governs the fluidity and motion smoothness, resolution defines image clarity and detail. The choice between prioritizing one over the other depends on the specific application and viewing needs.
For dynamic and fast-moving visuals, focus on higher refresh rates. For applications requiring sharp and detailed visuals, prioritize high resolution. By balancing these parameters and considering factors like budget, application, and technology trends, you can select an LED display that perfectly suits your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Refresh rate impacts how smooth motion appears on the screen, while resolution affects the clarity and detail of the visuals.
Higher refresh rates reduce motion blur and input lag, providing a smoother and more responsive gaming experience.
High resolutions, such as 4K or 8K, are recommended for large displays to maintain image clarity and detail.
While it doesn’t affect clarity, a high refresh rate enhances motion smoothness, making videos appear more fluid.
Prioritize the parameter most relevant to your application—refresh rate for motion-heavy content and resolution for detailed imagery—while considering mid-range options that offer a balance of both.


